0грн.
CheckoutTemperature and humidity when growing cannabis

Growing medical or recreational cannabis (also known as marijuana, hemp, or CBD) requires high precision and control. That’s why climate control is a key factor both in greenhouses and indoor grow rooms.
Cannabis cultivation is subject to strict regulation: compliance with GMP, GAP, and other standards requires thorough environmental control. Without it, producing a high-quality product that meets industry requirements is impossible.
The goal of every grower is to obtain the highest quality, large buds with the desired cannabinoid and terpene profile, while completely eliminating the risk of mold.
Why climate control matters
To achieve consistent, high-quality yields, cannabis/marijuana seeds are grown in controlled environments: greenhouses, grow rooms, or even grow tents. This allows you to regulate:
- Lighting;
- Temperature;
- Humidity;
- Airflow;
- CO₂ levels.
Lighting for cannabis

The role of light
Light is essential for photosynthesis. Like any plant, cannabis has specific preferences for light intensity and spectrum.
Day and night cycles
Cannabis is a photoperiod-sensitive plant. This means it enters the flowering phase based on the length of the dark period. To induce flowering, cannabis requires prolonged darkness.
Indoors, this is easy to manage. In greenhouses, blackout systems are used.
Typically:
- Vegetative stage: long days, short nights;
- Flowering stage: short days, long nights.
Types of lamps and energy efficiency
Modern setups use LED lamps — they consume less power compared to HPS (high-pressure sodium) lights. However, even LED lights produce heat, especially in commercial setups.
Temperature control

Optimal temperature: 18–26 °C (65–80 °F). This promotes healthy growth, proper bud formation, and reduces stress.
Temperature control tools include:
- HVAC systems;
- Air conditioners;
- Heat pumps;
- Hot/cold water systems.
Temperature is closely linked to humidity and lighting. Managing these factors is the foundation of climate control.
Humidity control in cannabis cultivation
Optimal humidity levels
Ideal relative humidity depends on the growth stage:
- Vegetative stage: 40–70%;
- Flowering stage: reduced humidity.
Ideal VPD (Vapor Pressure Deficit):
- Vegetative stage: 0.8–1.1 kPa;
- Flowering stage: 1.0–1.5 kPa.
Preventing mold
The main threats to cannabis are fungi:
- Botrytis (bud rot);
- Powdery mildew.
They spread rapidly, especially in high humidity, and can destroy entire crops. The use of fungicides is strictly limited — especially in medical production.
The best protection is prevention: maintain a dry environment and avoid condensation.
Dehumidification
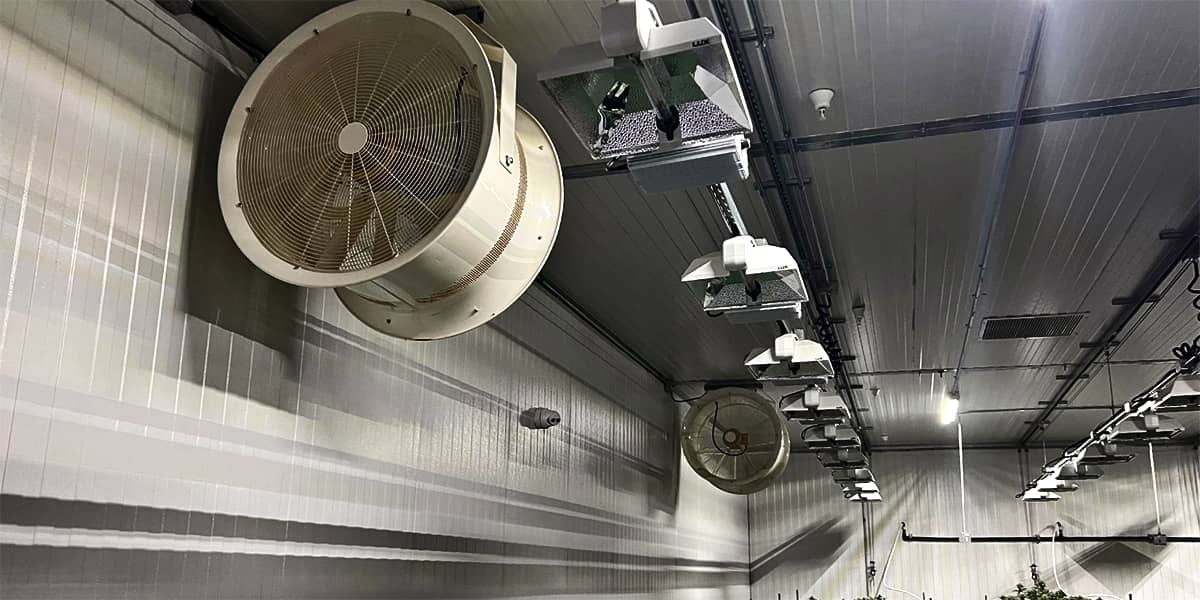

Dehumidifiers
The most effective method is using dehumidifiers such as DryGair. They use heat exchangers to extract moisture from the air.
HVAC vs. Dehumidifiers
HVAC systems are primarily designed for temperature control and only partially manage humidity. To reduce humidity with HVAC, it must run continuously, which is inefficient and costly.
Disadvantages of HVAC:
- High energy consumption;
- Need for additional equipment;
- Increased maintenance and installation costs.
Using specialized dehumidifiers is a more economical and consistent solution.
Airflow and Circulation
Even with perfect temperature and humidity, air movement is essential — especially in dense canopies. Within the foliage and buds, microclimates with high humidity can form.
To prevent this, use:
- Horizontal and vertical fans;
- Air circulation systems built into dehumidifiers (like DryGair) that distribute dry air evenly.
This helps:
- Prevent mold;
- Ensure uniform growing conditions;
- Improve crop quality.
Carbon Dioxide (CO₂) in Cultivation
CO₂ is essential for photosynthesis. Increasing its concentration to 1000 ppm in indoor environments promotes faster growth and development (if sufficient light and water are provided).
Why to Avoid Ventilation
Many growers use exhaust fans to reduce humidity. However, this leads to heat and CO₂ loss, increasing heating and CO₂ supplementation costs.
Using dehumidifiers allows you to:
- Avoid ventilation;
- Retain heat and CO₂;
- Reduce costs;
- Improve environmental control.
Conclusion
Cannabis cultivation is a business. And to run a successful business, you need to balance costs and product quality. The more precise your climate control — the higher your yields and the lower your losses. The better your quality — the greater your profits. The less mold — the fewer risks. Choosing the right equipment and environmental control systems determines not just plant growth, but the success of your entire operation.