0.00€
CheckoutHow does potassium deficiency differ from a deficiency of other macronutrients?
Potassium is one of the most important macronutrients necessary for normal crop growth and development. Potassium plays a role in plants by regulating water balance, activating enzymes, and synthesizing proteins and sugars.
The role of potassium in plants and its importance
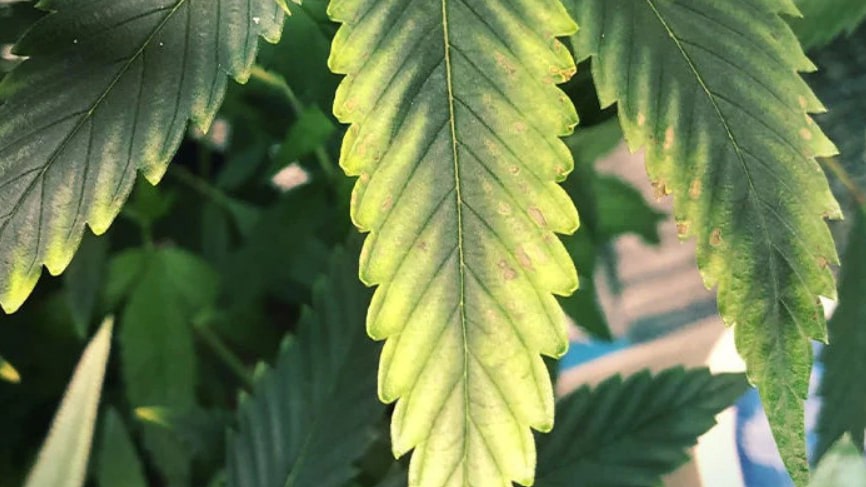

Potassium is one of the key macronutrients without which crops cannot develop properly. Its main function is to regulate water metabolism and activate a variety of enzymatic reactions. That is why potassium's functions in plants are directly related to photosynthesis, sugar synthesis, and the formation of starch and proteins. Thanks to this, potassium affects not only growth, but also the quality of fruits, their taste, and shelf life.
Unlike nitrogen and phosphorus, which primarily stimulate growth and root formation, potassium plays a protective role: it strengthens cell walls, making plants more resistant to diseases and adverse conditions. Adequate potassium nutrition allows plants to survive drought, temperature fluctuations, and even reduce stress from pest attacks.
It is important to note that a lack of potassium in the soil is often accompanied by complex problems. For example, if there is an excess of magnesium, the roots absorb potassium less efficiently, and the plant begins to suffer from hidden potassium starvation. Outwardly, this may look like yellowing or drying of the edges of the leaves, even though fertilizers are applied regularly. This is why agronomists emphasize the need for a balanced application of all macronutrients, not just nitrogen and phosphorus.
Thus, it can be said that potassium is the element responsible for the “vitality” of plants, while the other macronutrients perform more specialized tasks..
Signs of potassium deficiency and its diagnosis
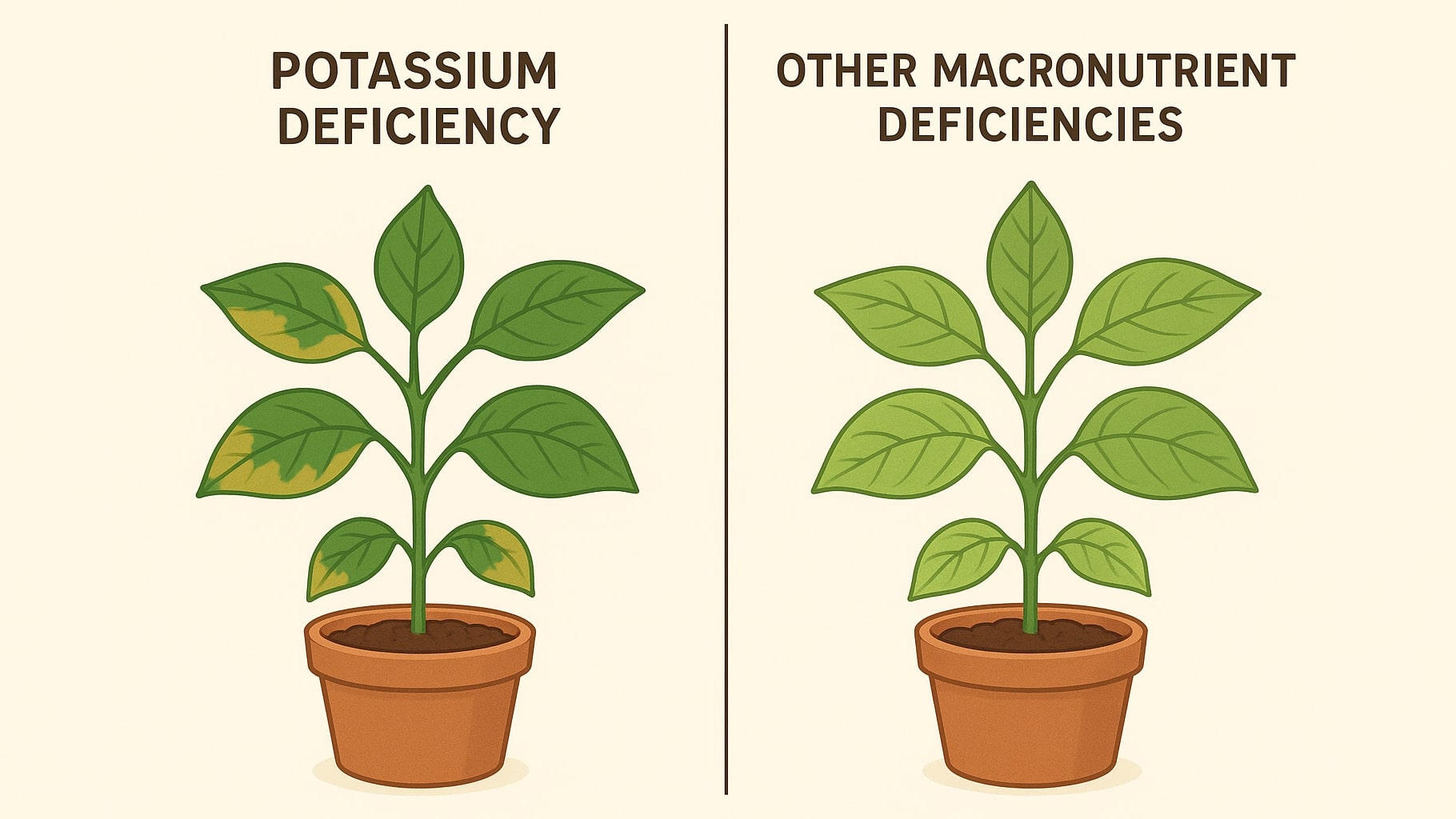
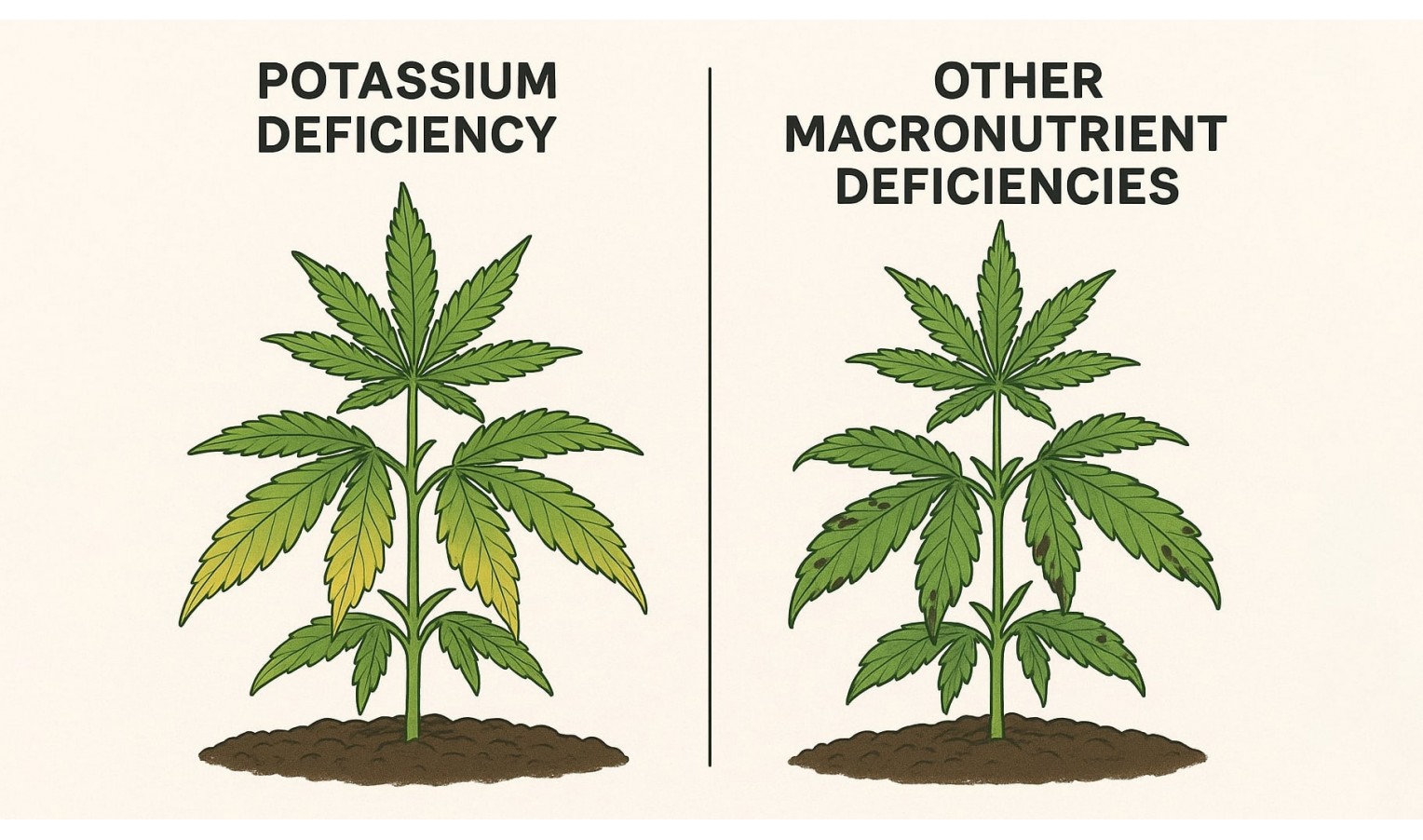
Potassium deficiency can be identified by a number of characteristic signs that distinguish it from other types of macroelement deficiencies. It is important to remember that symptoms may appear gradually, starting with the lower leaves, and can easily be confused with other nutritional disorders.
The main signs of potassium deficiency:
- Leaf margin burn – first, the tissue at the edges of the leaf blade turns light yellow, then browns and dies.
- Marble pattern on leaves – the veins remain green, while the interveinal tissue gradually deteriorates.
- Decreased turgor – plants look sluggish even with sufficient watering.
- Slow growth and low fruit quality – berries, fruits, or vegetables are small and have reduced sugar content.
- Increased susceptibility to disease – without potassium, the crop is less resistant to fungal infections.
For a correct diagnosis of potassium deficiency, it is necessary to compare the symptoms with other options:
- Nitrogen deficiency manifests itself as uniform yellowing of older leaves.
- Phosphorus deficiency is accompanied by a purple or crimson tint to the foliage.
- Magnesium deficiency causes interveinal chlorosis, which is often confused with potassium deficiency.
- Calcium deficiency affects young leaves, which curl and become deformed.
- Sulfur deficiency is similar to nitrogen deficiency, but manifests itself primarily on the upper part of the plant.
To avoid errors in assessment, experienced agronomists use a comprehensive approach: they analyze visual symptoms, check soil composition, and adjust nutrition. For example, when growing vegetables indoors or in hydroponics, testing the solution for macronutrient content is often used.
Interestingly, even crops such as hemp show similar signs of potassium deficiency. During germination and cultivation, especially when using autoflowering hemp seeds, a lack of potassium immediately affects the growth rate and density of inflorescences. This once again confirms the universal importance of this element for all plants.
Differences between potassium deficiency and deficiency of other macronutrients

The main difference between potassium deficiency and other forms of nutrient deficiency lies in its effect on water balance and stress resistance. While nitrogen, phosphorus, and calcium are more often associated with tissue growth and plant structure formation, potassium is responsible for regulating all metabolic processes, from photosynthesis to nutrient transport.
To better illustrate how potassium deficiency differs from other forms of nutrient deficiency, consider the following comparative table:
| Macronutrient | Main functions | Symptoms of deficiency | Features of assimilation |
| Potassium | Water balance, immunity, sugar synthesis | Leaf tip burn, stunted growth, reduced yield | May be blocked by excess magnesium or excess iron |
| Nitrogen | Green mass growth, protein synthesis | Yellowing of old leaves, poor development | Easily washed out of the soil |
| Phosphorus | Energy exchange, root development | Purple tint of leaves, delayed flowering | Poorly absorbed in cold soil |
| Magnesium | The center of the chlorophyll molecule, photosynthesis | Interveinal chlorosis, pale leaves | Competes with calcium and potassium |
| Calcium | Formation of cell walls, growth of young tissues | Deformation of upper leaves, fruit rot | Not available for acidic soils |
| Sulfur | Synthesis of amino acids and proteins | Yellowing of young leaves, slow growth | Often found on poor sandy soils |
This table helps to understand that differences in macronutrient deficiencies are directly related to their role in plant biochemistry. For example, with a potassium deficiency, the plant loses its ability to retain moisture and becomes vulnerable to drought, while with a nitrogen deficiency, it is the growth of green mass that suffers.
It is important to consider the opposite situation: sometimes signs of starvation appear not because of a deficiency, but because of a blockage of the element. For example, an excess of iron can interfere with the absorption of phosphorus and potassium, leading to false symptoms of deficiency. Therefore, agronomists always recommend analyzing not only visible signs, but also the balance of all elements in the soil.
Attention! Sunny Seeds does not encourage you to grow cannabis and does not promote it in any way. Growing cannabis is prohibited by Ukrainian law. This article is intended solely for scientific and informational purposes.