0грн.
CheckoutPhosphorus in cannabis cultivation: a key nutrient

Phosphorus is one of the key nutrients, without which full plant development is impossible. It is responsible for forming a strong root system, photosynthesis processes, metabolism, and directly affects flowering and yield. For those involved in cannabis cultivation, phosphorus level control plays a crucial role: it determines growth speed, bud size, and final product quality.
Phosphorus is found in many cannabis fertilizers, especially in bloom formulas and root stimulators. Proper use of this macronutrient can significantly increase yield and produce more resinous and aromatic buds.
The phosphorus cycle in nature
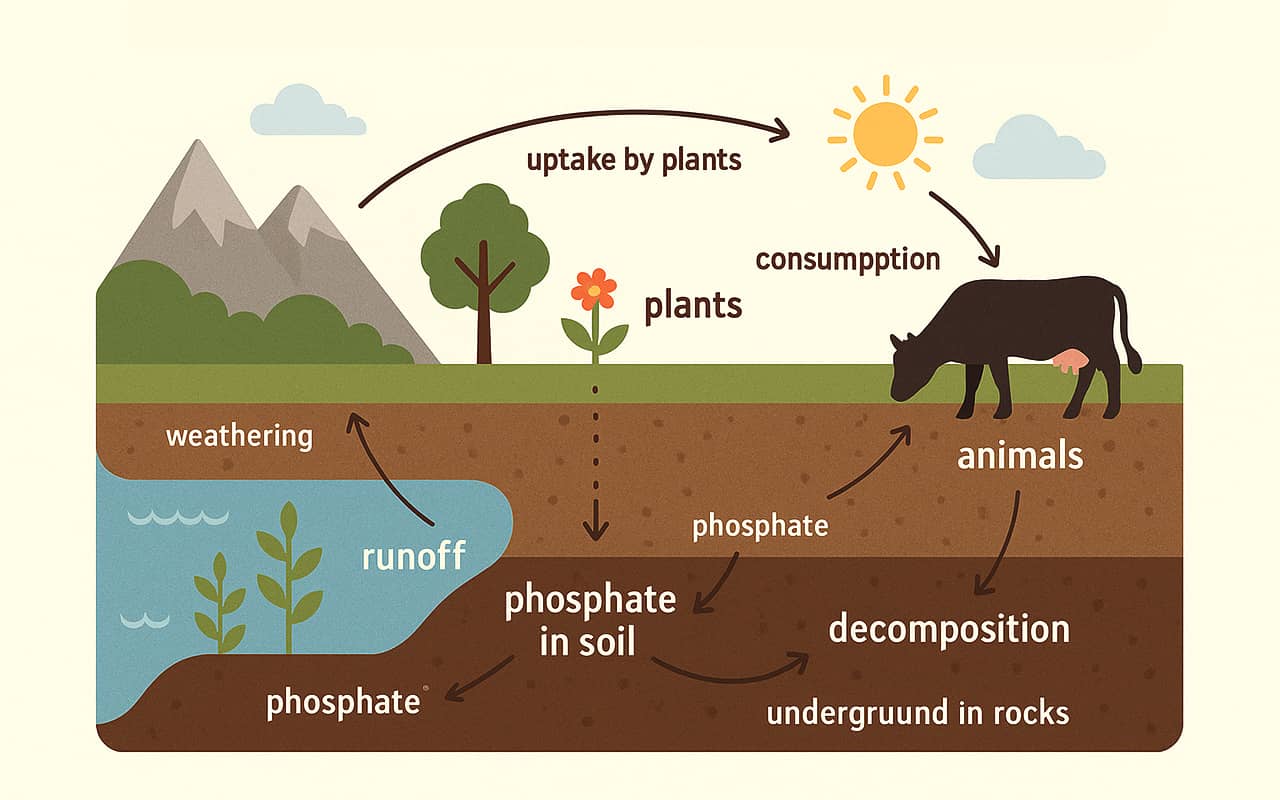
Before a plant can absorb phosphorus, it goes through a complex biogeochemical cycle. In nature, phosphorus exists as phosphates — compounds formed from decomposed organic matter or phosphate rocks. Plants absorb it from the soil, animals feed on these plants, and then phosphorus returns to the soil through organic waste and is processed by microorganisms. Part of the mineral ends up in seas and oceans, where it is absorbed by algae and marine fauna. It returns to land in two ways: through the droppings of seabirds and fish, or as a result of tectonic processes, which can take thousands of years.
Why cannabis needs phosphorus
Phosphorus is especially important for growing marijuana indoors and in hydroponics, as it ensures:
- rapid root development and better water uptake from the substrate;
- stronger stems and resistance to diseases;
- shorter vegetative stage and faster transition to flowering;
- higher yields and improved bud quality;
- accumulation of sugars and starches, enhancing the flavor and aroma of the harvest.
This is why phosphorus dosage is always considered in cannabis feeding plans — its deficiency or excess immediately affects plant health.
Phosphorus deficiency in marijuana

When a plant does not receive enough of this nutrient, it starts drawing reserves from older leaves. As a result:
- growth slows down, new leaves become smaller;
- petioles and stems take on a purple hue;
- leaves darken, curl, and eventually die off;
- buds remain small and weak;
- plants become more vulnerable to fungi and pests.
If the problem is not resolved in time, it can lead to massive leaf drop and even plant death.
How to fix phosphorus deficiency
To restore normal nutrition, you should:
- Check and adjust the substrate pH (soil — 5.8–6.5; hydroponics — 5.5–6.2);
- Flush the roots with water at a stable pH level;
- Apply a light watering with a phosphorus fertilizer (both organic and mineral types are suitable, with mineral ones working faster).
This strategy allows plants to resume proper nutrient uptake and continue active growth.
Excess phosphorus in plants
It is important to remember that overfeeding with phosphorus is also harmful. Excess phosphorus blocks zinc and iron uptake, causes leaf deformation, and reduces crop quality. Therefore, cannabis fertilizers should always be chosen according to the growth phase, and nutrient solution concentration must be controlled.
Conclusion
In cannabis seeds cultivation, phosphorus is one of the key nutrients. It ensures growth, flowering, and harvest quality, but only in the right balance. Deficiency leads to slowed development and weakened plants, while excess blocks other essential elements. Proper fertilizer use and pH control will help achieve healthy plants and maximum yields of aromatic buds.