0грн.
CheckoutCannabis growing: nitrogen deficiency and excess

Nitrogen (N) is one of the main macronutrients essential for successful cannabis cultivation. It is responsible for the synthesis of proteins, amino acids, enzymes, and chlorophyll — essentially for the growth and development of the entire plant. Thanks to sufficient nitrogen levels, cannabis has lush green leaves, develops rapidly during the vegetative phase, and builds a strong immune system. However, this element has two sides: deficiency sharply slows development, while excess leads to toxicity that reduces crop quality.
The Role of Nitrogen in Cannabis
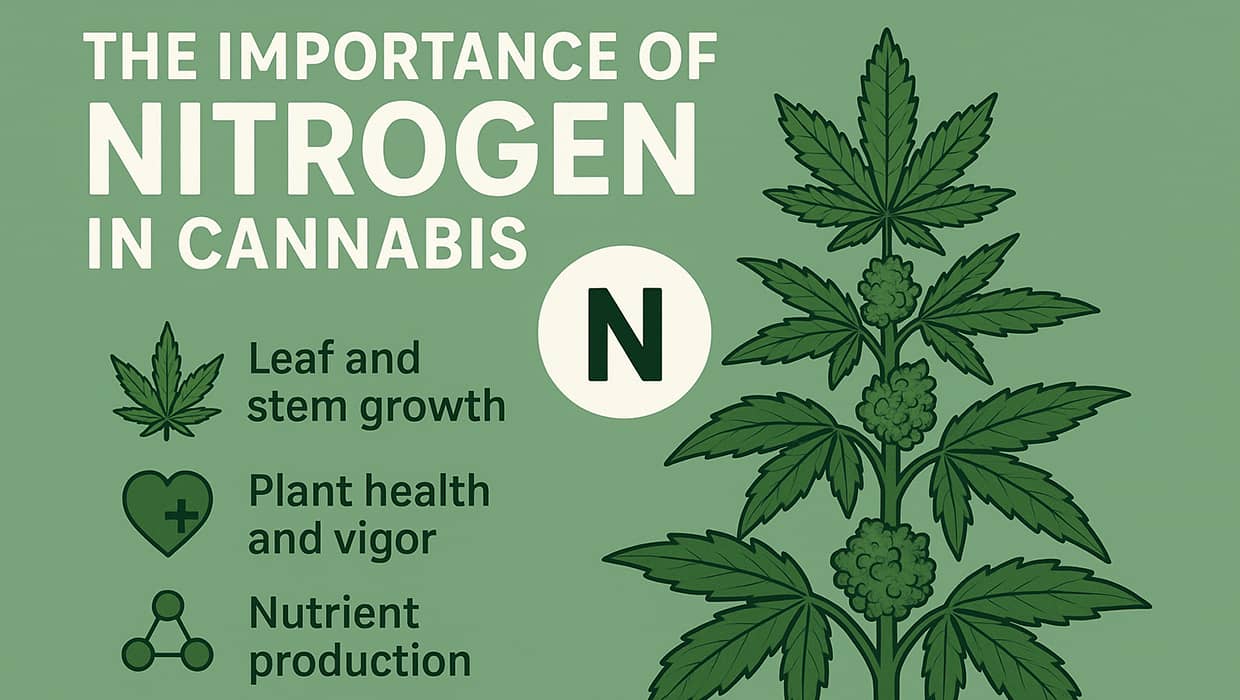
Throughout the plant’s life, nitrogen is involved in producing chlorophyll — the pigment that drives photosynthesis, providing energy for growth and the formation of new cells. In addition, it supports the production of nucleic acids and enzymes that regulate all vital processes. Therefore, a lack of nitrogen in soil or nutrient solution immediately affects the overall health of the plants.
In fertilizers, nitrogen occurs in three main forms:
- ammonium (NH₄⁺), which is quickly absorbed but may cause overdose;
- nitrate (NO₃-), which acts more slowly and safely;
- organic, which breaks down thanks to soil microflora and is suitable for organic growers.
Most mineral and liquid fertilizers combine these forms to provide stable and balanced nutrition throughout the cycle.
Nitrogen Deficiency in Cannabis: Signs and Consequences
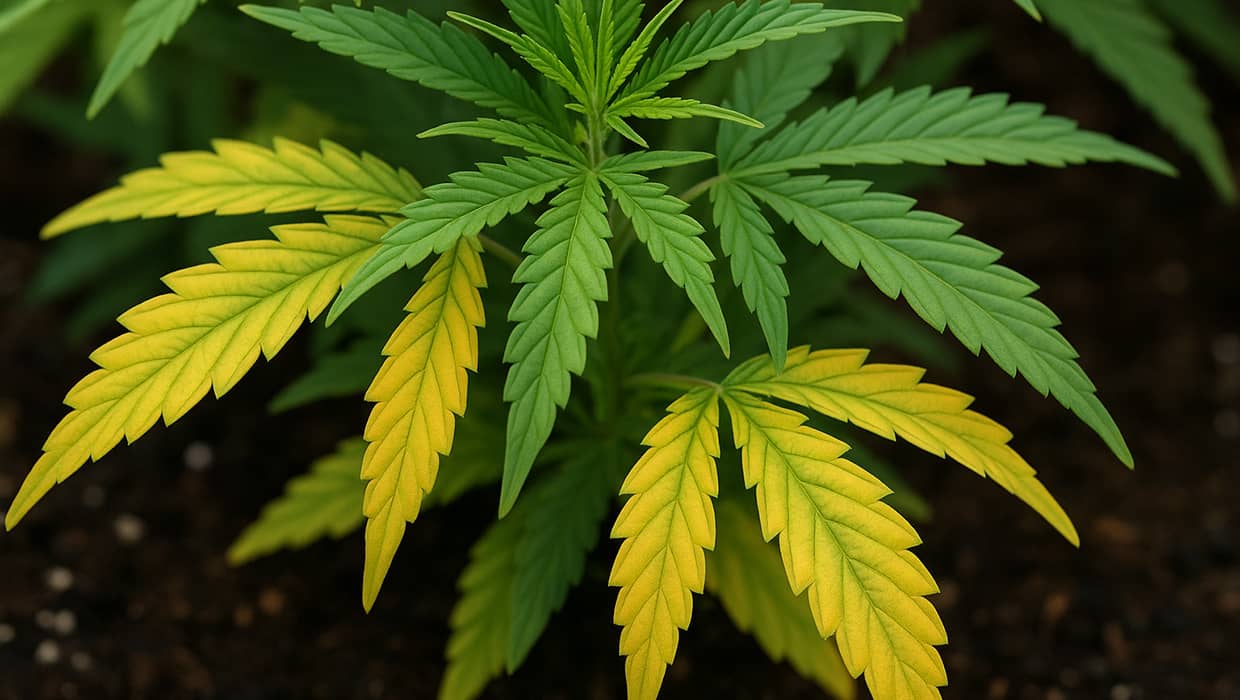

Nitrogen deficiency develops gradually. First, lower older leaves turn yellow because the plant transfers its nitrogen reserves to new growth points. Then the leaves lose their rich color, becoming pale green or almost lemon yellow. As the deficiency progresses, growth slows, branches thin, and yields decrease significantly. Buds become less resinous, with weaker aroma and effect. In advanced cases, massive leaf drop occurs, and the plant fails to produce a full harvest.
To correct the situation, growers add liquid nitrogen fertilizers or organic infusions — such as fish emulsion or blood meal. A key factor is pH: in soil it should be 6.0–6.5, and in hydroponics 5.5–6.0, otherwise even applied nitrogen will not be absorbed.
Nitrogen Excess in Cannabis: Risks
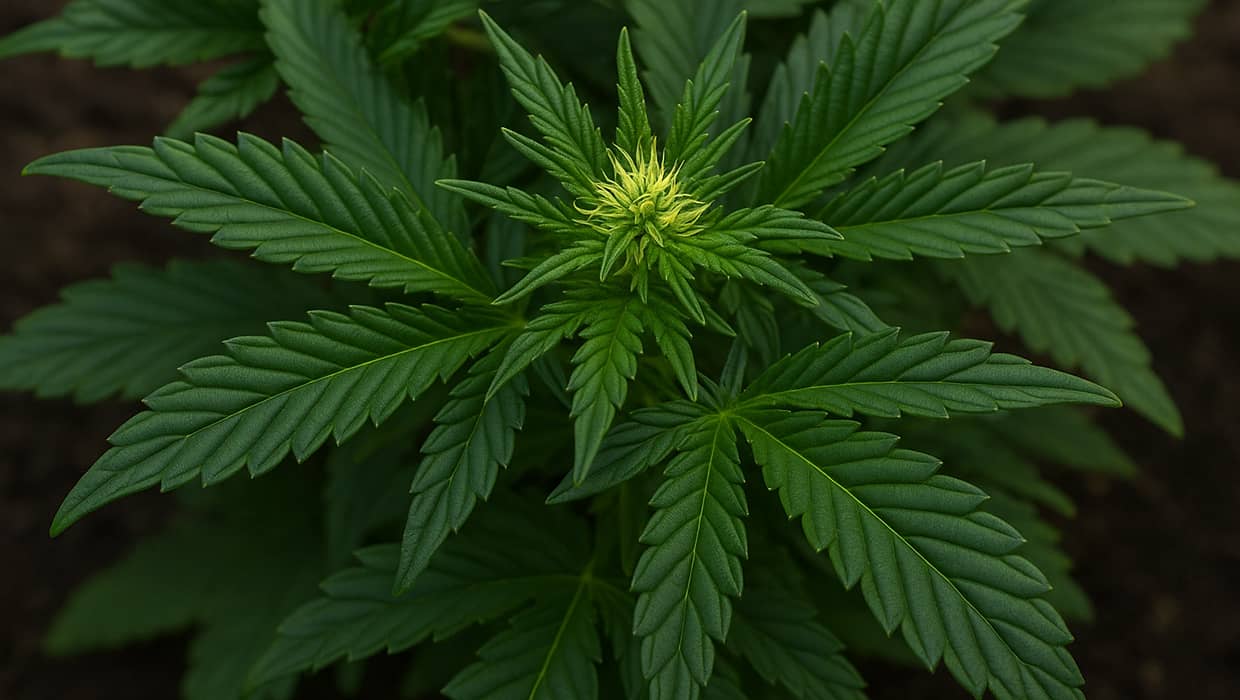

Overfeeding with nitrogen-rich fertilizers often happens to beginners who try to “boost” plant growth. Main symptoms of excess include:
- leaves become very dark green and glossy;
- edges curl downward in a “claw” shape;
- stems weaken and flowering is delayed;
- buds form small and airy, with poor burning quality;
- aroma and flavor of flowers become less pronounced.
Excess nitrogen makes plants more vulnerable to pests and fungal infections. In addition, overfed cannabis has a poorer cannabinoid and terpene profile, directly affecting the strength and effect of the final product. Correction begins with flushing the substrate with low EC water in amounts three times the pot’s volume.
In severe cases, enzyme products are used to help remove salt buildup faster. During flowering, base nitrogen fertilizers are removed, leaving only a PK complex without nitrogen so that the plant can consume its excess while continuing to develop buds.
Recovery After Stress
Cannabis responds fairly quickly to nutrition correction, but the speed of recovery depends on growth phase and cultivation method. In hydroponics, improvements are visible within a few days, whereas in soil with organic fertilizers the process may take a week or longer. During the vegetative period, plants can fully recover from mild deficiency or excess, but during flowering any mistake has a much stronger impact on crop quality.
Conclusion
Nitrogen is essential for the vegetative growth of cannabis, but it is also the nutrient that growers encounter the most common problems with. A deficiency leads to stunted growth and crop loss, while an excess leads to poorer bud quality and reduced plant stability. The secret to success in growing cannabis seeds lies in balance: using fertilizers with the right combination of nitrogen forms, controlling pH levels, and carefully monitoring symptoms on the leaves. This is the only way to get a stable yield of healthy and aromatic cannabis without unnecessary losses.
This text is for informational purposes only and does not contain cultivation instructions. Any actions with plants of the genus Cannabis must comply with the laws of your country/region.